Given the robust nature of learning sciences research, this website is best viewed on tablets and computers. A small screen experience is coming in the future.
On June 22, 2021, we will launch updated strategies for the Math PK-2 model, as well as additional updates to the Navigator that highlight equity, SEL, and culturally responsive teaching. To learn more, visit our Site Updates (available in the "About" menu at the top of any page).

Hover to see how factors connect to Long-term Memory. Then click connected factors to explore strategies related to multiple factors.
Long-term Memory can store information indefinitely. We can move skills and knowledge into Long-term Memory by repeatedly practicing and using them. The Background Knowledge and Vocabulary stored in Long-term Memory provide students with a strong foundation for their reading and writing assignments.
Physically acting out a text or enacting major themes from texts enhances reading comprehension, particularly as texts become more complex.
Project-based learning (PBL) actively engages learners in authentic tasks designed to create products that answer a given question or solve a problem.
For adolescent learners, the Composition process can become more robust, as learners begin to express ideas through multiple media, which includes visual, audio, and digital production.
When students express information visually, they are activating more cognitive processes while problem solving and increasing their experience with alternate texts.
During reading, giving students the opportunity to explain their thinking process aloud allows them to recognize the strategies they use, solidify their comprehension, and move knowledge into their Long-term Memory.
Visiting places connected to classroom learning provides opportunities to deepen understanding through firsthand experiences.
Games help students practice their literacy skills in a fun, applied context.
When students write from a non-dominant or marginalized perspective, they consider and give voice to points of view that are often missing.
Response devices boost engagement by encouraging all students to answer every question.
Students practice making and finding meaning in texts through book discussions moderated by teachers to varying degrees.
Flexible grouping is a classroom practice that temporarily places students together in given groups to work together, with the purpose of achieving a given learning goal or activity.
When peers are able to work together to plan, draft, edit, and revise during the Composition process, their writing quality improves.
As students move through multimodal stations pertaining to a particular unit, the social and physical nature of the activity supports deeper understanding.
As students work with and process information by discussing, organizing, and sharing it together, they deepen their understanding.
When students provide constructive feedback on each other's work, they learn to give relevant suggestions, receive specific ways to improve their writing, and engage in Metacognition.
Having students teach their knowledge, skills, and understanding to their classmates strengthens learning and increases Motivation.
When students explain to others, they deepen their understanding and gain confidence in their learning.
Think-pair-share encourages meaningful student discussion by allowing for extra processing time and multiple shares.
Writing conferences allow students to fully immerse, share, reflect, and receive feedback during the writing process, promoting Motivation for continuing the sometimes lengthy revision process that occurs in the upper grades.
A mnemonic device is a creative way to support memory for new information using connections to current knowledge, for example by creating visuals, acronyms, or rhymes.
Providing a story or concept map prior to lessons or having students create their own maps during or after reading helps learners identify and organize key elements of a text.
Displaying academic Vocabulary on a word wall can reinforce key terms and concepts that students are learning.
When adolescents can connect and communicate with authentic audiences about their interests and values, reading and writing become more personally meaningful and relevant.
As part of a varied curriculum, explicit instruction in reading comprehension strategies from teachers can help older students use strategies meaningfully and flexibly.
Teaching students how to effectively search the internet is critical for helping them learn how to find accurate and relevant information and aids in developing information literacy.
Seeing and using new words repeatedly and in many contexts is critical for Vocabulary acquisition.
Explicitly teaching strategies for planning, writing, and revising texts improves students' writing quality.
Interpreting and composing discipline-specific texts requires tailoring literacy strategies, like annotating or asking questions, to the disciplinary goals and practices.
During guided inquiry, teachers foster student autonomy by designing lessons centered on meaningful questions in which students locate, analyze, and present relevant information on their own or in small groups.
Independent reading promotes literacy by emphasizing student choice with teacher support in selecting books, as well as setting the expectations that everyone is a reader.
Instruction in multiple formats allows students to activate different cognitive skills and Background Knowledge that are necessary to remember procedural and content information.
Providing multiple texts on the same topic or theme allows students to interact with multiple perspectives and develop their critical thinking skills.
When teachers ask questions or have students create questions before introducing a text, they activate student interest and help them assess what they already know about a given topic.
Providing guiding prompts and questions for students to use when reading or participating in discussions deepens their understanding of texts and gives them space to question and grapple with issues of power, justice, and equity.
When teachers provide students with model texts for their writing, they learn to identify effective elements to incorporate into their own writing.
Teachers can provide individualized support through one-on-one conferences to assess reading comprehension, understanding of content, and spark further interest in reading.
A strengths-based approach is one where educators intentionally identify, communicate, and harness students' assets, across many aspects of the whole child, in order to empower them to flourish.
Checklists and rubrics help students understand expectations as they navigate more complex tasks and assignments.
Journaling allows students to reflect on their thinking and feelings, process their learning, and connect new information to what they know, supporting their identity development and Sense of Belonging.
Student reflection on learning, particularly when done collaboratively, is critical for moving knowledge of content and strategies into Long-term Memory.
When students monitor their comprehension, performance, and use of strategies when reading and writing, they build their Metacognition and actively participate in the reading process.
When annotating, students engage deeply with a text and make their thinking visible while reading.
Pre-assessments are tools or activities used before instruction begins to help educators understand what students already know, understand, or can do—and where they may need support.
Audiobooks allow students to hear fluent reading and to experience books that may be above their reading skills.
Communication boards are displays of graphics (e.g., pictures, symbols, illustrations) and/or words where learners can gesture or point to the displays to extend their expressive language potential.
Dictionaries and thesauruses can serve as resources for students to expand their Vocabulary knowledge, as they provide easy access to definitions and similar words to help students remember words and meanings more readily.
Dictation, also referred to as speech-to-text, an assistive communication technology that translates voice dictation to digital text, provides students with transcription difficulties the opportunity to participate in the writing process by allowing them to use their voice to generate and record ideas.
Adding gestures and motions to complement learning activates more cognitive processes for recall and understanding, particularly within content area instruction.
Brain breaks that include movement allow learners to refresh their thinking and focus on learning new information.
Connecting information to music and dance can support Short-term and Long-term Memory by engaging auditory processes, Emotions, and physical activity.
Transforming written text into audio supports learning by activating different parts of a learner's brain for comprehension.
Visual supports, like text magnification, colored overlays, and text manipulation, help students focus and properly track as they read.
Word sorts are multisensory activities that help learners identify patterns and group words based on different categories while promoting Vocabulary development.
Multiple display spaces promote collaboration by allowing groups to share information easily as they work.
Multiple writing surfaces promote collaboration by allowing groups to share information easily as they work.
Providing texts in braille, large font, and with text-to-speech allows learners with visual needs to access content.
Reading materials of varying complexity and levels are necessary for all students to experience success.
With figurative language and creative sentence structure, poetry supports the development of a deeper understanding of the different ways language makes meaning.
Daily review strengthens previous learning and can lead to fluent recall of information and application of skills.
Opportunities for students to practice skills in context, with teacher support and also independently, helps to move concepts and ideas into Long-term Memory.
Practicing until achieving several error-free attempts is critical for retention.
Increasing how much and how frequently students write improves both their writing quality and content knowledge.
Students build their confidence, strategy use, and comprehension by reading and rereading multiple texts.
Having students verbally repeat information such as instructions ensures they have heard the information and supports remembering, particularly for those students who struggle with Attention.
Chunking involves breaking texts down into more manageable pieces to help learners focus their Attention while reading and to comprehend text more effectively.
Teaching students how to systematically evaluate sources prepares them to navigate in an increasingly complex, digital world.
Providing constructive feedback supports students' writing development by letting them know how to improve their writing.
By talking through their thinking at each step of a process, teachers can model what learning looks like.
Reading aloud to adolescents models Reading Fluency as texts become more complex and disciplinary in nature and therefore, more difficult to understand.
Using texts to discuss complex emotions and perspectives with students can help them see how they influence behavior and draw their own personal connections.
Wait time, or think time, of three or more seconds after posing a question increases how many students volunteer and the length and accuracy of their responses.
Advance graphic organizers link prior knowledge to upcoming learning to help students anticipate and understand the structure of new information.
Visualizing how ideas fit together helps students construct meaning and strengthens their recall.
Using visual aids, such as pictures, diagrams, and charts, allows for additional processing time and supports learners by breaking down content and skills into more manageable parts.
Sentence frames or stems provide language support for students' writing and participation in academic discussions.
Providing visuals to introduce, support, or review instruction activates more cognitive processes to support learning.
Selecting culturally responsive reading materials, including multicultural and diverse texts, is critical for supporting all students.
Learning about students' cultures and connecting them to instructional practices helps foster a Sense of Belonging and mitigate Stereotype Threat.
Translanguaging is a flexible classroom practice enabling students to listen, speak, read, and write across their multiple languages or dialects, even if the teacher does not have formal knowledge of these additional languages.
 Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
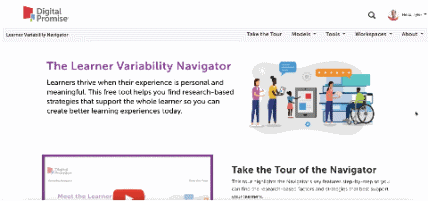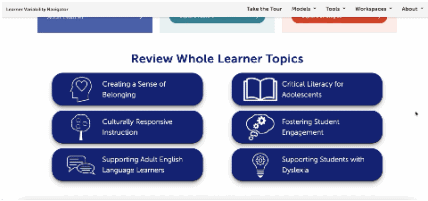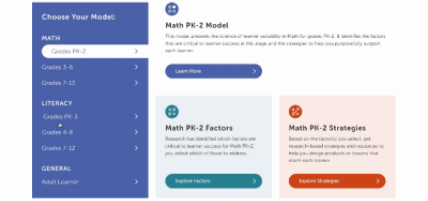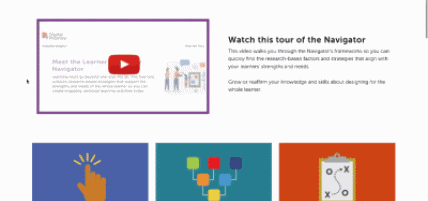
This is our homepage. You can access many of the features of the Navigator here, and learn more about how learner variability intersects with topics in education and learning. To start, select a content area – we call them Learner Models – to visit a factor map.
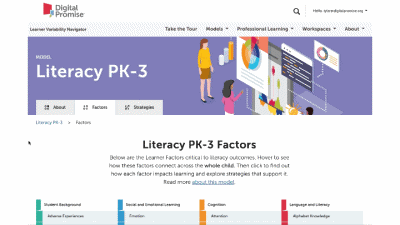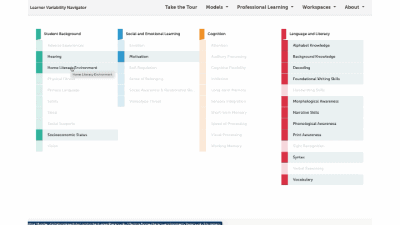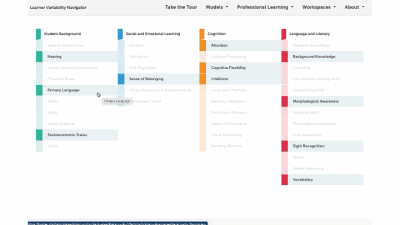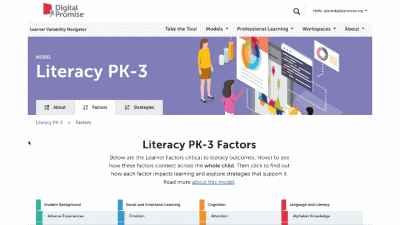
Factor maps show research-based concepts, "factors," that likely impact learning. They are organized into four categories: Learner Background, Social and Emotional Learning, Cognition, and Content Area. The map is interactive. Move your cursor over a factor to see connected factors. Select any factor to visit its summary page. We'll look at factor summary pages next.
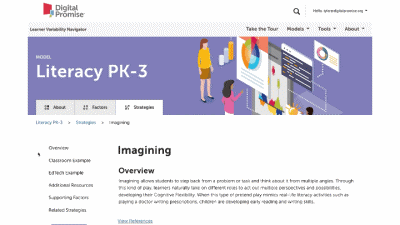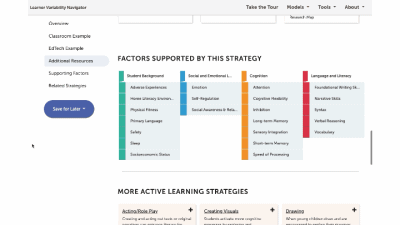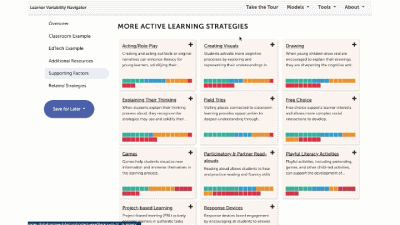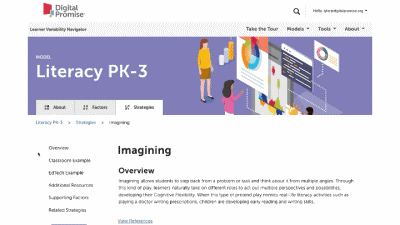
This is a factor summary page. It provides a brief definition and review of the factor, a factor connections diagram, additional resources, and strategies that support this factor. On the strategy card, the multi-colored boxes show all the factors that it supports. Select a strategy to visit its summary page.
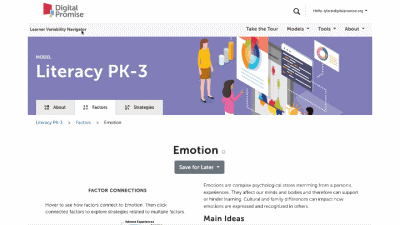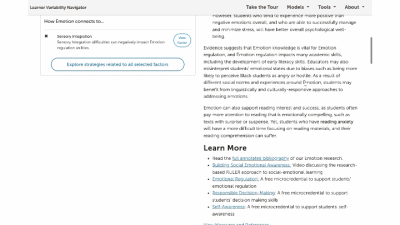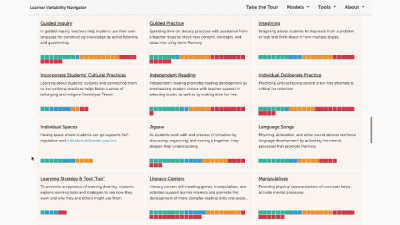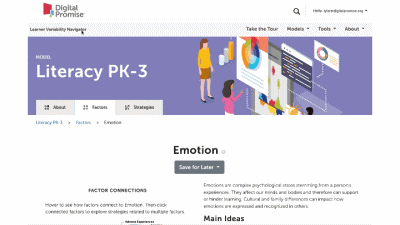
Strategy summary pages have an overview, information about using the strategy in different learning environments, resources of interest, the factors this strategy supports, and related strategies you can explore. To view all the strategies in a content area, use the strategies tab at the top of the page. We'll look at all the Strategies for this learner model next.
The strategy page shows ALL of the strategies for that learner model. You can select factors of interest for you or your learners, and it will narrow the strategies to only those that match all of the factors selected. This makes it easy to find key strategies to better design for learner variability. Again, select the strategy name to visit its summary page.
Are you sure you want to delete this Workspace?
Enter the email address of the person you want to share with. This person will be granted access to this workspace and will be able to view and edit it.
Adjust the permissions of your Workspace.
This Workspace is .
This Workspace's Reflection Area is .
Learner variability is the recognition that each learner is a unique constellation of strengths and challenges that are interconnected across the whole child. Understanding these connections and how they vary according to context is essential for meeting the needs of each learner.
It disrupts the notion of a one-size-fits all education. Understanding learner variability helps educators embrace both students’ struggles and strengths as we connect practice to uplifting the whole learner.
Throughout the site, we talk about "factors" and "strategies." Factors are concepts research suggests have an impact on how people learn. Strategies are the approaches to teaching and learning that can be used to support people in how they learn best.
Use the Learner Centered Design Tool to build a workspace. Go to Learner Centered Design Tool.
Or, create a new blank workspace for your product or project.
Use one of the guided tools to build a workspace.
Or, create a new blank workspace for your product or project.
Make a copy of this workspace.
Redirecting soon...
Generating summary page
Loading...
On this page, using your heatmap, you will be asked to select factors to further explore, and then select new strategies you might incorporate into upcoming instruction. Once done, click “Show Summary" to view your Design Summary Report.
On this page, using your heatmap, you will be asked to select factors to further explore, and then select new strategies you might incorporate into upcoming instruction. Once done, click “Show Report” to view your Design Summary Report.
By selecting "Show Report" you will be taken to the Assessment Summary Page. Once created, you will not be able to edit your report. If you select cancel below, you can continue to edit your factor and strategy selections.
Announcement here
Item successfully added to workspace!
Issue adding item to workspace. Please refresh the page and try again.
Learner variability is the recognition that each learner is a unique constellation of strengths and challenges that are interconnected across the whole child. Understanding these connections and how they vary according to context is essential for meeting the needs of each learner. It embraces both students’ struggles and strengths. It considers the whole child.
Throughout the site, we talk about "factors" and "strategies." Factors are concepts research suggests have an impact on how people learn. Strategies are the approaches to teaching and learning that can be used to support people in how they learn best.
The Learner Variability Navigator is a free, online tool that translates the science of learner variability into factor maps and strategies that highlight connections across the whole learner. This puts the science of learning at teachers' fingertips, empowering them to understand their own practice and support each learner.