Lateral Reading
Overview
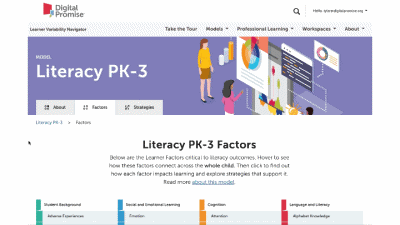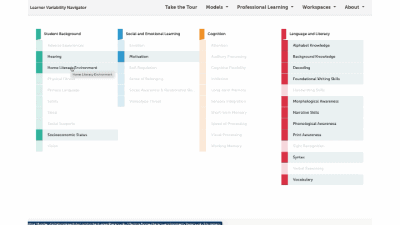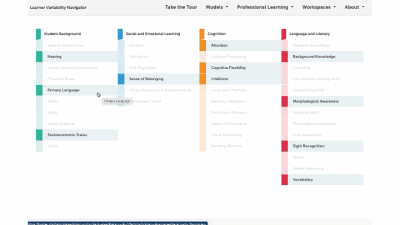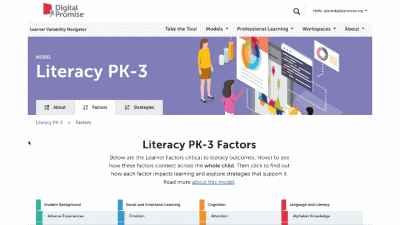
Lateral reading refers to a specific type of media literacy used by professional fact-checkers to ascertain the credibility of digital information. Lateral reading focuses on evaluating the trustworthiness of an unfamiliar website by identifying potential bias, misinformation, and fact-finding through a review of outside sources. It promotes Critical Thinking by teaching students to evaluate digital information by moving beyond the original source rather than simply evaluating the website based on its appearance, URL, or content, which is “vertical reading”. While most informational reading standards focus on a vertical reading approach to analyzing sources, the ability to critically analyze digital information is essential for developing Civic Mindedness that can inform participation in school, the community, and in a democratic society.
Example: Use This Strategy In in the Classroom
Design It into Your Product
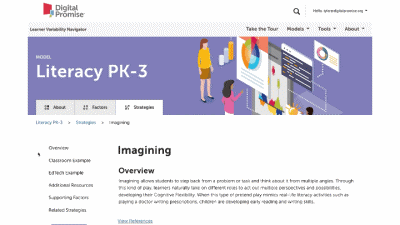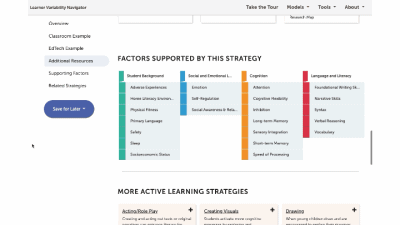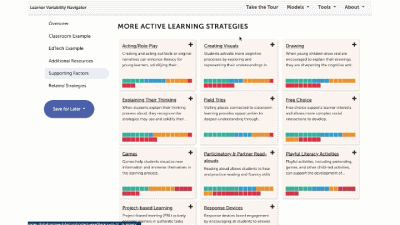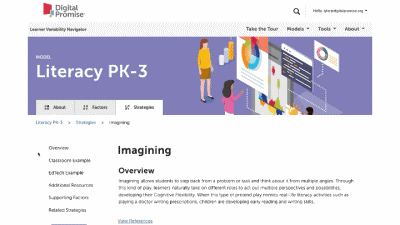
Factors Supported by this Strategy
More Teacher Modeling & Support Strategies
Providing instructional steps clearly and concisely can help learners understand classroom expectations, reduce cognitive load, and complete tasks more efficiently.
Building positive and trusting relationships with learners fosters a Sense of Belonging, safety, and engagement, laying the groundwork for academic, cognitive, and social-emotional growth.
Discussing emotions with children consists of supporting their ability to identify, label, and manage their feelings.
Self-advocacy is the ability of an individual to understand and effectively express and assert their own rights, needs, desires, and interests.
Providing students a voice in their learning is critical for making learning meaningful.