Verbal Repetition
Overview
Having students verbally repeat information such as instructions ensures they have heard and supports remembering. With verbal repetition, learners also can personalize and interact with information, activating multiple brain pathways to move knowledge from Short- to Long-term Memory.
Example: Use This Strategy In in the Classroom
Design It into Your Product
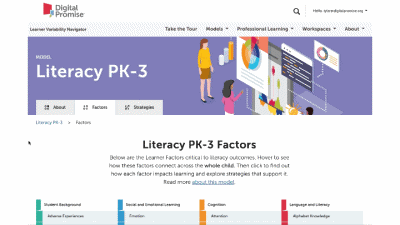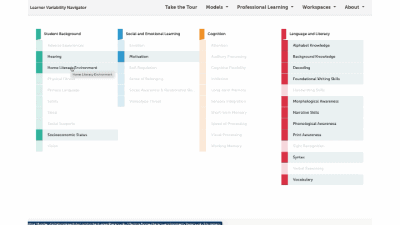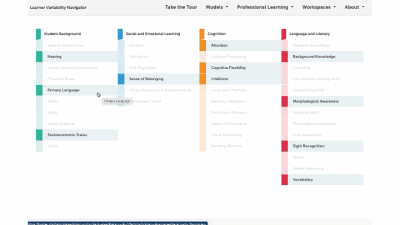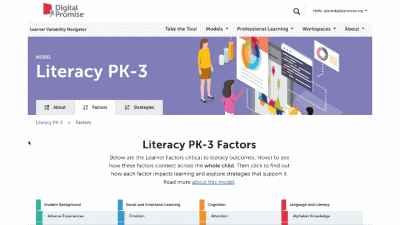
Factors Supported by this Strategy
Mathematics
More Repetition Strategies
Cumulative Review
Continual use of foundational skills with different problems reinforces a conceptual understanding of math skills.
Daily Review
Daily review strengthens previous learning and can lead to fluent recall.
Guided Practice
Spending time with new content helps move concepts and ideas into Long-term Memory.
Individual Deliberate Practice
Practicing until achieving several error-free attempts is critical for retention.