Given the robust nature of learning sciences research, this website is best viewed on tablets and computers. A small screen experience is coming in the future.
On June 22, 2021, we will launch updated strategies for the Math PK-2 model, as well as additional updates to the Navigator that highlight equity, SEL, and culturally responsive teaching. To learn more, visit our Site Updates (available in the "About" menu at the top of any page).

Hover to see how factors connect to Social Supports. Then click connected factors to explore strategies related to multiple factors.
Social Supports are the perception and presence of a support network available to help a person if needed. People are social creatures, and our well being is in part based on having supportive friends and family. The power of Social Supports extends to learning: a learner's perception of the strength of the support they have is a key contributor to their emotional and academic success..
Simulations and immersive virtual environments provide authentic learning at a level that can spark curiosity and deeper understanding by engaging multiple senses in exploration.
For adults, the Composition process can become more robust when learners can express ideas through multiple media, which includes visual, audio, and digital production.
Inquiry-based learning is centered around open-ended questions posed by instructors and/or the learners themselves and fosters a Learner Mindset.
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a learner-centered multidisciplinary approach focused on real world applications using active learning methods.
The opportunity to observe peers or experts in action or participate in shadowing can provide a unique and authentic learning experience that often involves questioning, metacognitive thinking, and Problem Solving while providing Social Supports.
Networking and supporting adult learners in expanding their social networks provide access to additional resources and Social Supports, which can impact their trajectory and Motivation.
Beginning meetings with check-ins and maximizing opportunities for informal check-ins, whether live or online, can foster a sense of Belonging while building Social Supports.
Flexible grouping is a classroom practice that temporarily places learners' together in given groups to work together, with the purpose of achieving a given learning goal or activity.
Learning in social contexts has been shown to have significant effects on comprehension of material and retention of new information into Long-term Memory.
When learners provide constructive feedback on each other's work, they reflect on their own understanding, learn to give relevant suggestions, receive specific ways to improve, and engage in Metacognition.
Giving learners the opportunity to share their knowledge, skills, and understanding with others strengthens learning and increases Motivation while also building Social Supports.
Adult learners can self-organize into groups called communities of practice to engage in longer-term examination of a topic to build deeper understanding.
When adults can connect and communicate with authentic audiences about their interests and values, learning becomes more personally meaningful and relevant.
In an increasingly digital world, adults who struggle with using technology can benefit from direct instruction for an array of digital tools.
Mindfulness is a practice to create internal balance and a sense of being present in the moment.
When annotating, learners engage deeply with a text and make their thinking visible while reading, which supports Foundational Reading Skills.
Journaling allows learners to reflect on their thinking and feelings, process their learning, and connect new information to what they know and their practical experiences.
Speech-to-text takes the input from voice recognition and produces text.
A strengths-based approach is one where educators intentionally identify, communicate, and harness learners' assets to empower them to flourish.
Chunking involves breaking texts down into more manageable pieces to help learners focus their Attention while reading and to comprehend text more effectively.
Understanding adults' lived experiences and cultural backgrounds and connecting them to instructional practices helps all learners feel like valued members of the community.
Immediate feedback can improve a learner's confidence, self-awareness and enthusiasm for learning, which leads to increased Motivation.
Adult learners benefit from knowing there is an instructor available to provide support as needed, especially during asynchronous learning.
Discussions about race can range from celebrating the importance of diversity to understanding the impact of racism from the perspective of those who have been historically marginalized.
Developing empathy in educators and in learners is an iterative process that requires taking the time to understand and honor others' perspectives.
Developing cultural awareness as an educator is an ongoing process that includes building empathy for diverse learners, intentionally recognizing how one's own identity intersects with learners' identities, and creating an awareness of how the environment can impact learners' Sense of Belonging.
A first step to supporting learners is truly understanding who they are.
 Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This is our homepage. You can access many of the features of the Navigator here, and learn more about how learner variability intersects with topics in education and learning. To start, select a content area – we call them Learner Models – to visit a factor map.
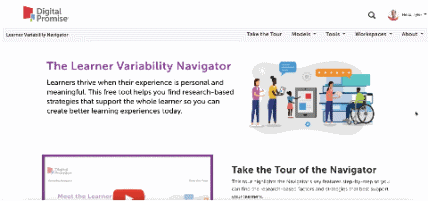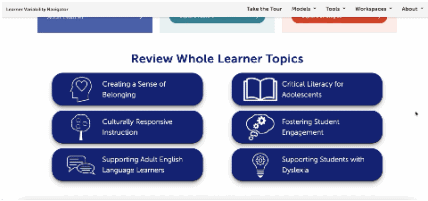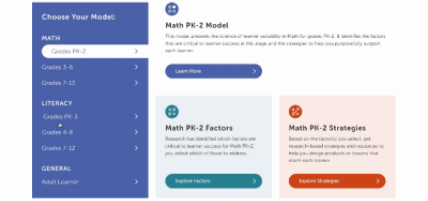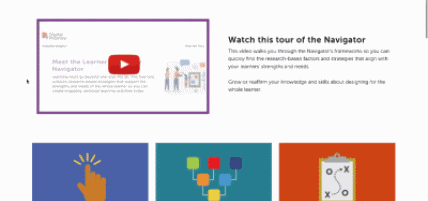
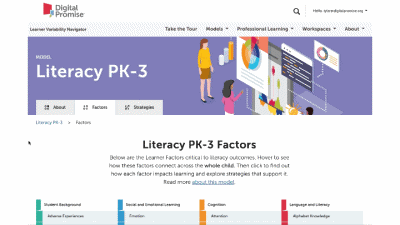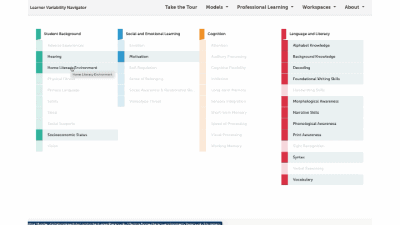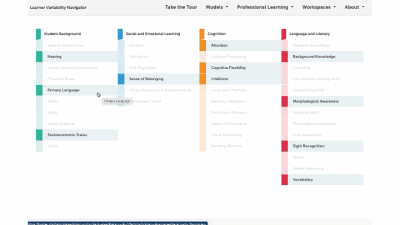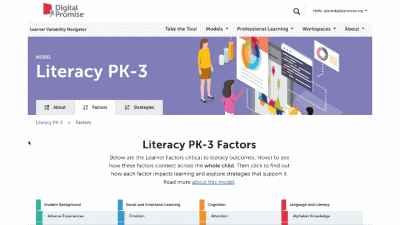
Factor maps show research-based concepts, "factors," that likely impact learning. They are organized into four categories: Learner Background, Social and Emotional Learning, Cognition, and Content Area. The map is interactive. Move your cursor over a factor to see connected factors. Select any factor to visit its summary page. We'll look at factor summary pages next.
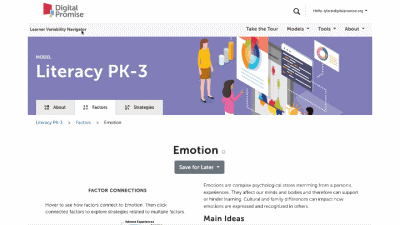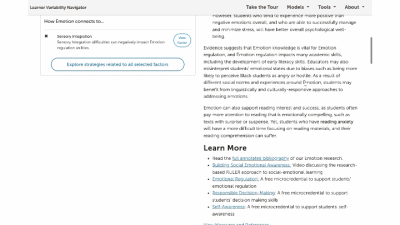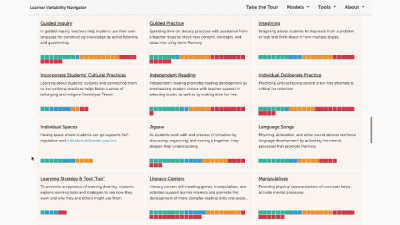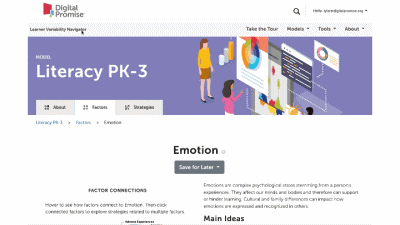
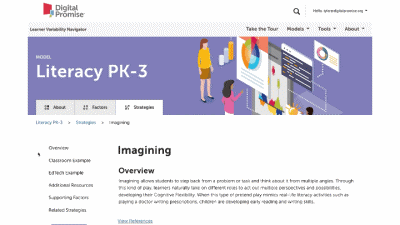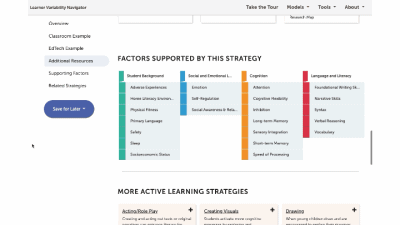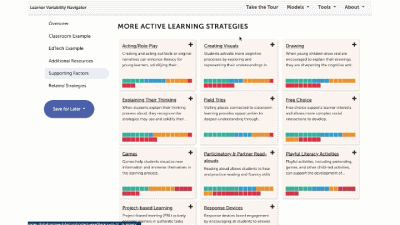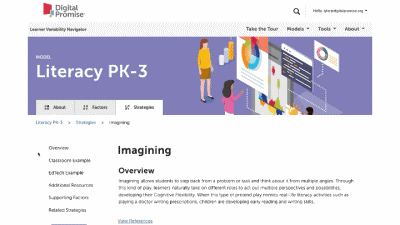
This is a factor summary page. It provides a brief definition and review of the factor, a factor connections diagram, additional resources, and strategies that support this factor. On the strategy card, the multi-colored boxes show all the factors that it supports. Select a strategy to visit its summary page.
Strategy summary pages have an overview, information about using the strategy in different learning environments, resources of interest, the factors this strategy supports, and related strategies you can explore. To view all the strategies in a content area, use the strategies tab at the top of the page. We'll look at all the Strategies for this learner model next.
The strategy page shows ALL of the strategies for that learner model. You can select factors of interest for you or your learners, and it will narrow the strategies to only those that match all of the factors selected. This makes it easy to find key strategies to better design for learner variability. Again, select the strategy name to visit its summary page.
Are you sure you want to delete this Workspace?
Enter the email address of the person you want to share with. This person will be granted access to this workspace and will be able to view and edit it.
Adjust the permissions of your Workspace.
This Workspace is .
This Workspace's Reflection Area is .
Learner variability is the recognition that each learner is a unique constellation of strengths and challenges that are interconnected across the whole child. Understanding these connections and how they vary according to context is essential for meeting the needs of each learner.
It disrupts the notion of a one-size-fits all education. Understanding learner variability helps educators embrace both students’ struggles and strengths as we connect practice to uplifting the whole learner.
Throughout the site, we talk about "factors" and "strategies." Factors are concepts research suggests have an impact on how people learn. Strategies are the approaches to teaching and learning that can be used to support people in how they learn best.
Use the Learner Centered Design Tool to build a workspace. Go to Learner Centered Design Tool.
Or, create a new blank workspace for your product or project.
Use one of the guided tools to build a workspace.
Or, create a new blank workspace for your product or project.
Make a copy of this workspace.
Redirecting soon...
Generating summary page
Loading...
On this page, using your heatmap, you will be asked to select factors to further explore, and then select new strategies you might incorporate into upcoming instruction. Once done, click “Show Summary" to view your Design Summary Report.
On this page, using your heatmap, you will be asked to select factors to further explore, and then select new strategies you might incorporate into upcoming instruction. Once done, click “Show Report” to view your Design Summary Report.
By selecting "Show Report" you will be taken to the Assessment Summary Page. Once created, you will not be able to edit your report. If you select cancel below, you can continue to edit your factor and strategy selections.
Announcement here
Item successfully added to workspace!
Issue adding item to workspace. Please refresh the page and try again.
Learner variability is the recognition that each learner is a unique constellation of strengths and challenges that are interconnected across the whole child. Understanding these connections and how they vary according to context is essential for meeting the needs of each learner. It embraces both students’ struggles and strengths. It considers the whole child.
Throughout the site, we talk about "factors" and "strategies." Factors are concepts research suggests have an impact on how people learn. Strategies are the approaches to teaching and learning that can be used to support people in how they learn best.
The Learner Variability Navigator is a free, online tool that translates the science of learner variability into factor maps and strategies that highlight connections across the whole learner. This puts the science of learning at teachers' fingertips, empowering them to understand their own practice and support each learner.