Simulations & Immersive Virtual Environments
Overview
Simulations and immersive virtual environments provide authentic learning at a level that can spark curiosity and deeper understanding by engaging multiple senses in exploration. Presence, immersion, and access to learning environments beyond the limits of geography provide rich learning opportunities that can mitigate the effects of Socioeconomic limitations, Adverse Experiences, and physical challenges. Being immersed in the learning environment can also improve Attention, Working Memory, transfer to Long-term Memory, and support the development of a Learner Mindset.
Use It in Your Learning Environment
The use of simulations and immersive virtual environments has been found to be particularly effective when paired with an inquiry-based approach to learning. Simulations can be categorized into three approaches in the work-based learning (WBL) environment allowing learners to practice the knowledge and skills they acquire in a real-world setting: simulation tools to teach specific skills or tasks, simulated workspaces to replicate a range of workplace expectations, and holistic experiences such as running an actual business in a given industry. What they and hybrid approaches have in common is the immersive learning opportunity that replaces or augments real world experiences through facilitated experiential learning. All immersive experiences, including AR, VR, and XR, support developing a Learner Mindset.
Augmented Reality (AR) technology overlays virtual objects into the real world. Effective uses of AR that align with Universal Design for Learning Principles include: adding QR codes to training materials, adding AR elements to electronic books, AR applications integrated with web technologies enhancing collaborative learning, using coloring and three dimensional imaging techniques, seeing step-by-step solutions, accessing inaccessible geographic spaces and locations, determining dangers and degrees of importance, and presenting natural events and experiences that cannot be experienced in the physical world. When designing products with AR, it is important to consider the effect on cognitive load, which could impact Working Memory.
Virtual Reality (VR) technology makes it possible to create an authentic, immersive learning environment with the potential to improve Attention, engagement, spatial awareness, and Long-term Memory. Since VR instills a sense of wonder and surprise, it can foster intrinsic Motivation leading to higher academic persistence and interest. Intercultural learning can take place in immersive environments to build intercultural communication without the need to travel to be immersed in another culture. VR can provide access by breaking the limitations of time and space while creating an environment in which people from different cultures interact.
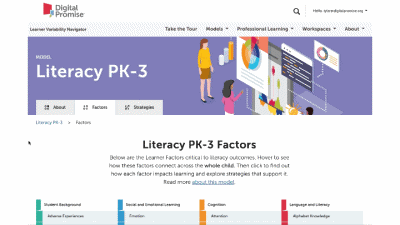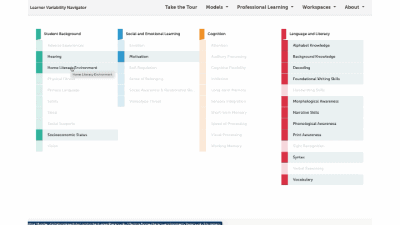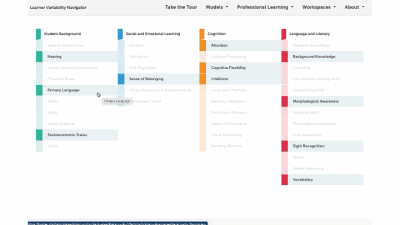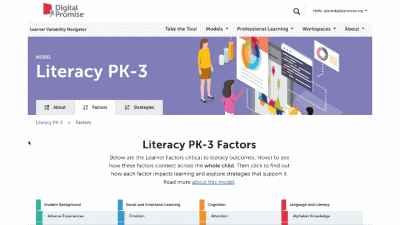
Factors Supported by this Strategy
More Active Learning Strategies
Experts can answer questions and provide vocabulary, processes, feedback, and scaffolds to help learners deepen their understanding.
Case studies support authentic, active learning experiences centered around real world situations that present an account of a particular set of circumstances for learners to engage with.
When learners process and express information visually, they are activating more cognitive processes while Problem Solving.
When preparing for and executing a debate, learners analyze, form, and express verbal arguments, fostering their critical thinking skills, an essential component of Problem Solving.
Debriefing is the intentional discussion immediately following a learning experience which is especially important after simulation-based learning.
Analyzing errors is especially beneficial in helping learners develop a Learner Mindset and critical thinking skills, which are a component of Problem Solving.
Networking and supporting adult learners in expanding their social networks provide access to additional resources and Social Supports, which can impact their trajectory and Motivation.
Experiential learning is learning by doing, which may include self-directed learning activities.
Giving learners the opportunity to explain their thinking process aloud helps them to solidify their comprehension, and move knowledge into their Long-term Memory.
Game-based learning is an active learning experience with clear objectives and measurable outcomes designed to be intrinsically game-like.
Inquiry-based learning is centered around open-ended questions posed by instructors and/or the learners themselves and fosters a Learner Mindset.
For adults, the Composition process can become more robust when learners can express ideas through multiple media, which includes visual, audio, and digital production.
Effective note-taking during lectures or reading directs learners' Attention to the relevant information, helping them identify key concepts, understand links between ideas and retain information better in their Long-term Memory.
The opportunity to observe peers or experts in action or participate in shadowing can provide a unique and authentic learning experience that often involves questioning, metacognitive thinking, and Problem Solving while providing Social Supports.
When learners provide constructive feedback on each other's work, they reflect on their own understanding, learn to give relevant suggestions, receive specific ways to improve, and engage in Metacognition.
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a learner-centered multidisciplinary approach focused on real world applications using active learning methods.
Skills sprints are focused, real world learning experiences for teams in which participants learn new skills while directly designing, developing, or delivering something to their organization.
Analyzing short video clips, replays of important aspects, and videos of oneself applying what has been learned can improve Metacognition and Long-term Memory while fostering a Learner Mindset.
Analyzing and discussing solutions to problems helps students develop a deeper understanding of Problem Solving processes and Numeracy skills.