Read-Alouds
Overview
Read-alouds are an instructional practice in which teachers read aloud from a text to students, modeling fluent reading, asking questions, and actively engaging with students to enhance their understanding. Read-alouds can make texts more accessible and bridge the gap between students' reading abilities and the expectations of school curriculum, especially in middle school where literacy demands increase from elementary school across content areas. When teachers engage in read-alouds, they help reduce the cognitive load on students, allowing them to redirect their cognitive resources from decoding text to comprehension and vocabulary acquisition.It is especially important when using read-alouds in middle school that teachers employ interactive questioning techniques to prevent students from becoming passive learners. During interactive read-alouds, educators ask questions surrounding the text and encourage learners to engage in meaningful discussion which can include working through difficult vocabulary. Conversations surrounding read-alouds can support learners' Creativity and Curiosity about the topics and help them integrate their Background Knowledge in the classroom as they take an active role in the learning process. Through these read-aloud activities, learners can develop language and literacy skills, including strengthening their Communication and Critical Thinking skills. Read-aloud presentation of text positively affects reading comprehension of individuals with learning disabilities and language acquisition of multilingual learners.
Example: Use This Strategy In in the Classroom
Design It into Your Product
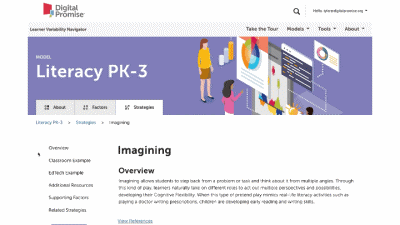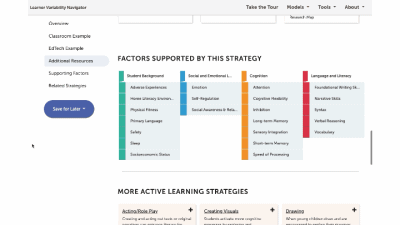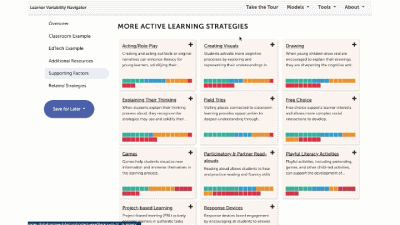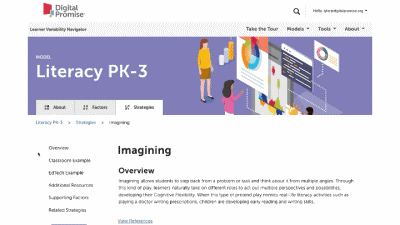
Factors Supported by this Strategy
More Instructional Approaches Strategies
Flipped learning is when the delivery of traditional content (i.e., lectures, and videos) occurs outside of the classroom, allowing class time to be used for more active and application-based activities.
In guided inquiry, teachers scaffold student learning and help students use their own language to construct knowledge by active listening and questioning.
Multimodal teaching and learning provide opportunities for students to engage with the same content through different sensory modalities, such as visual, auditory, and tactile.
Retrieval practice requires students to access information, or get information “out” from Long-term memory in order to support better retention and understanding.
Spaced practice is a learning strategy that deliberately spaces out learning or study sessions over varying periods of time, with the purpose of increasing retention, understanding, and long-term knowledge acquisition.
A strengths-based approach is one where educators intentionally identify, communicate, and harness students' assets, across many aspects of the whole child, in order to empower them to flourish.
Supported independent reading, sometimes called Scaffolded Silent Reading, is when teachers scaffold and monitor learners' independent reading time, offering students a choice of accessible texts, and periodic check-in's with individual students to provide guidance and accountability.