Given the robust nature of learning sciences research, this website is best viewed on tablets and computers. A small screen experience is coming in the future.
On June 22, 2021, we will launch updated strategies for the Math PK-2 model, as well as additional updates to the Navigator that highlight equity, SEL, and culturally responsive teaching. To learn more, visit our Site Updates (available in the "About" menu at the top of any page).

Hover to see how factors connect to Attention. Then click connected factors to explore strategies related to multiple factors.
Attention is the ability to focus on a specific task without being distracted. Attention helps students become better problem-solvers by allowing them to focus on and thoughtfully practice their developing math skills. Importantly, attentional control often varies based on the context, including interest in the topic, task difficulty, and task duration
Students activate more cognitive processes by exploring and representing their understandings in visual form.
Analyzing incorrect worked examples is especially beneficial for helping students develop a conceptual understanding of mathematical processes.
Project-based learning (PBL) actively engages learners in authentic tasks designed to create products that answer a given question or solve a problem.
When students explain their thinking process aloud with guidance in response to questions or prompts, they recognize the strategies they use and solidify their understanding.
Math games allow students to practice many math skills in a fun, applied context.
Response devices boost engagement by encouraging all students to answer every question.
When students create their own number and word problems, they connect math concepts to their background knowledge and lived experiences.
Analyzing and discussing solved problems helps students develop a deeper understanding of abstract mathematical processes.
As students solve problems in a group, they learn new strategies and practice communicating their mathematical thinking.
Flexible grouping is a classroom practice that temporarily places students together in given groups to work together, with the purpose of achieving a given learning goal or activity.
As students walk through stations working in small groups, the social and physical nature of the learning supports deeper understanding.
As students work with and process information by discussing, organizing, and sharing it together, they deepen their understanding.
Having students teach their knowledge, skills, and understanding to their classmates strengthens learning.
Students deepen their understanding and gain confidence in their learning when they explain to and receive feedback from others.
Students deepen their math understanding as they use and hear others use specific math language in informal ways.
Rhyming, alliteration, and other sound devices reinforce math skills development by activating the mental processes that promote memory.
Respectful redirection, or error correction, outlines a clear and concise way that educators can provide feedback on behaviors that need immediate correction, in a positive manner.
Providing math tasks with high cognitive demand conveys high expectations for all students by challenging them to engage in higher-order thinking.
Knowing the language of math is critical because students must use this language to understand math concepts and determine calculations needed.
Thinking of and about patterns encourages learners to look for and understand the rules and relationships that are critical components of mathematical reasoning.
Discussing strategies for solving mathematics problems after initially letting students attempt to problem solve on their own helps them understand how to organize their mathematical thinking and intentionally tackle problems.
Teaching students to recognize common problem structures helps them transfer solution methods from familiar to unfamiliar problems.
In guided inquiry, teachers help students use their own language for constructing knowledge by active listening and questioning.
Math centers support learner interests and promote the development of more complex math skills and social interactions.
Through short but regular mindfulness activities, students develop their awareness and ability to focus.
Instruction in multiple formats allows students to activate different cognitive skills to understand and remember the steps they are to take in their math work.
When teachers connect math to the students' world, students see how math is relevant and applicable to their daily lives.
A strengths-based approach is one where educators intentionally identify, communicate, and harness students' assets, across many aspects of the whole child, in order to empower them to flourish.
Writing that encourages students to articulate their understanding of math concepts or explain math ideas helps deepen students' mathematical understanding.
Setting overall goals, as well as smaller goals as steps to reaching them, encourages consistent, achievable progress and helps students feel confident in their skills and abilities.
When students reframe negative thoughts and tell themselves kind self-statements, they practice positive self-talk.
Providing space and time for students to reflect is critical for moving what they have learned into Long-term Memory.
When students engage in a dialogue with themselves, they are able to orient, organize, and focus their thinking.
When students monitor their comprehension, behavior, or use of strategies, they build their Metacognition.
Pre-assessments are tools or activities used before instruction begins to help educators understand what students already know, understand, or can do—and where they may need support.
Adding motions to complement learning activates more cognitive processes for recall and understanding.
Communication boards are displays of graphics (e.g., pictures, symbols, illustrations) and/or words where learners can gesture or point to the displays to extend their expressive language potential.
Short breaks that include mindfulness quiet the brain to allow for improved thinking and emotional regulation.
Brain breaks that include movement allow learners to refresh their thinking and focus on learning new information.
Providing physical and virtual representations of numbers and math concepts helps activate mental processes.
Connecting information to music and dance can support Short-term and Long-term Memory by engaging auditory processes, Emotions, and physical activity.
Research shows physical activity improves focus and creativity.
Incorporating multiple senses with strategies like chewing gum, using a fidget, and sitting on a ball chair supports focus and Attention.
Using earplugs or headphones can increase focus and comfort.
Transforming written text into audio activates different parts of the brain to support learning.
Tossing a ball, beanbag, dice, or other small object activates physical focus in support of mental focus.
Visual supports, like text magnification, colored overlays, and guided reading strip, help students focus and properly track as they read.
When classrooms are intentionally designed to promote inclusion, belonging, and accessibility, they positively influence key learner factors, including Attention, Self-Regulation, Learner Mindset, and Sense of Belonging.
Multiple tables and chairs on wheels allow for setting up the classroom to support the desired learning outcomes of each activity.
Multiple display spaces help develop oral language skills as well as Social Awareness & Relationship Skills by allowing groups to share information easily as they work.
Multiple writing surfaces promote collaboration by allowing groups to share information easily as they work.
Decreasing extra audio input provides a focused learning environment.
Providing ways for students to meet their individual temperature needs supports focus and Self-regulation.
Spaces that are structured, organized, and clean provide increased room for collaboration and active learning.
Continual use of foundational skills with different problems reinforces a conceptual understanding of math skills.
Daily review strengthens previous learning and can lead to fluent recall.
Spending time with new content helps move concepts and ideas into Long-term Memory.
Having students verbally repeat information such as instructions ensures they have heard and supports remembering.
Content that is provided in clear, short chunks can support students' Working Memory.
Teachers can help students understand that learning involves effort, mistakes, and reflection by teaching them about their malleable brain and modeling their own learning process.
Attributing results to controllable aspects (strategy and effort) fosters students' beliefs in self.
By talking through their thinking at each step of a process, teachers can model what learning looks like.
Maintaining consistent classroom routines and schedules ensures that students are able to trust and predict what will happen next.
Providing students a voice in their learning is critical for making learning meaningful.
Visualizing how ideas fit together helps students construct meaning and strengthens recall.
Visual representations help students understand what a number represents as well as recognize relationships between numbers.
Sentence frames or stems can serve as language support to enrich students' participation in academic discussions.
Providing visuals to introduce, support, or review instruction activates more cognitive processes to support learning.
Learning about students' cultures and connecting them to instructional practices helps foster a sense of belonging and mitigate Stereotype Threat.
Translanguaging is a flexible classroom practice enabling students to listen, speak, read, and write across their multiple languages or dialects, even if the teacher does not have formal knowledge of these additional languages.
Checking in with learners, or taking the time to talk with individual learners about their experiences or goals, is important for fostering a positive classroom environment.
 Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
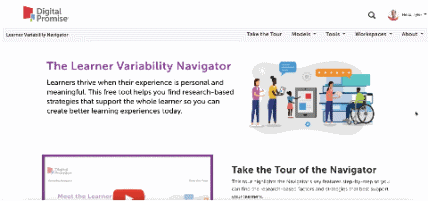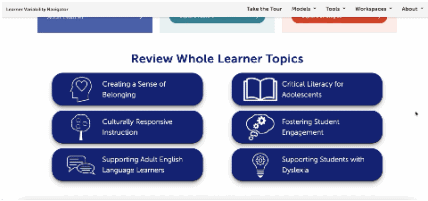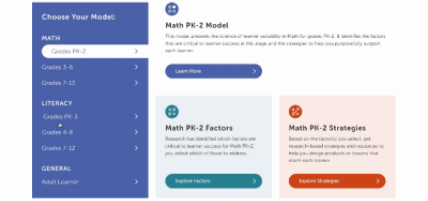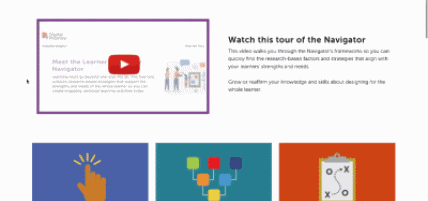
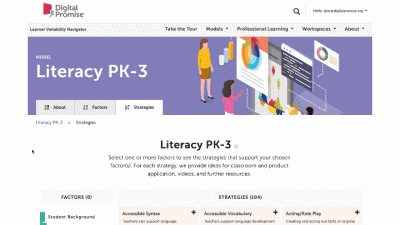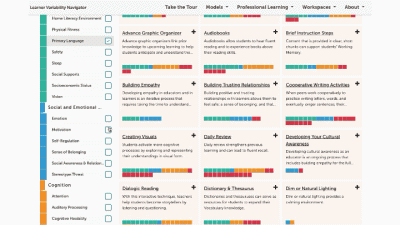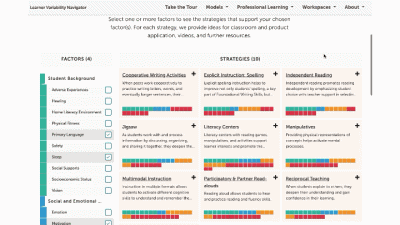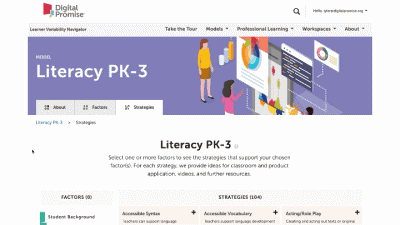
This is our homepage. You can access many of the features of the Navigator here, and learn more about how learner variability intersects with topics in education and learning. To start, select a content area – we call them Learner Models – to visit a factor map.
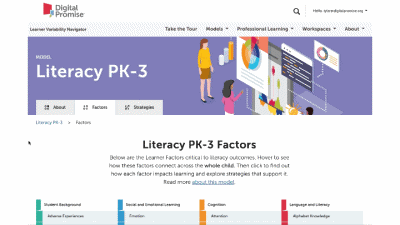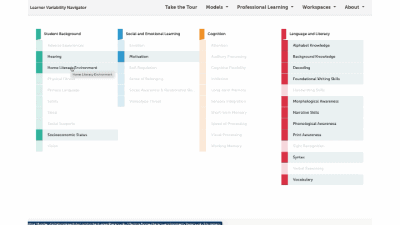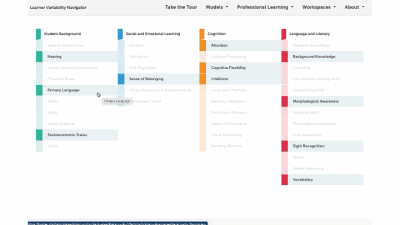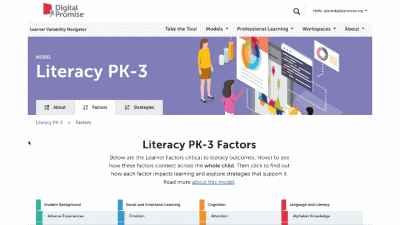
Factor maps show research-based concepts, "factors," that likely impact learning. They are organized into four categories: Learner Background, Social and Emotional Learning, Cognition, and Content Area. The map is interactive. Move your cursor over a factor to see connected factors. Select any factor to visit its summary page. We'll look at factor summary pages next.
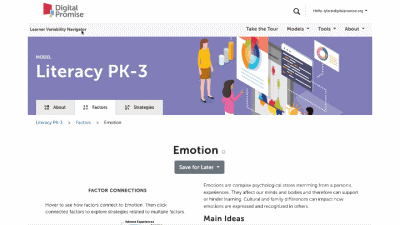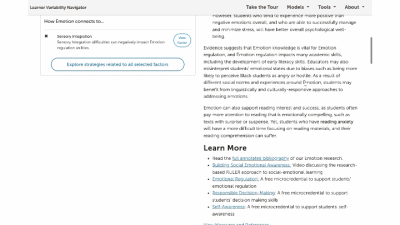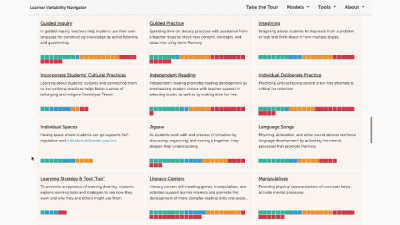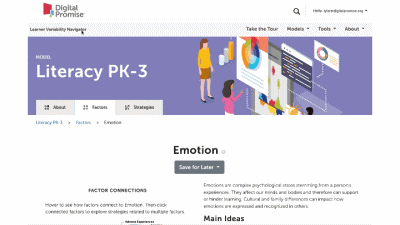
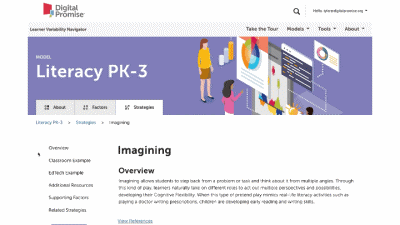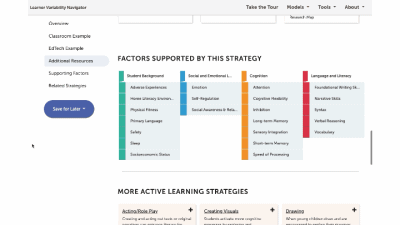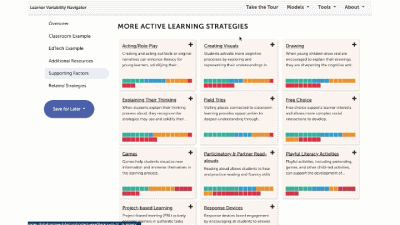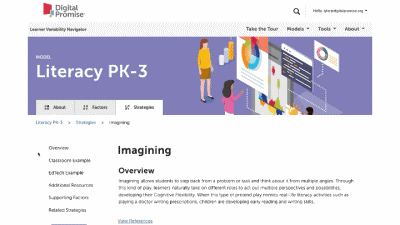
This is a factor summary page. It provides a brief definition and review of the factor, a factor connections diagram, additional resources, and strategies that support this factor. On the strategy card, the multi-colored boxes show all the factors that it supports. Select a strategy to visit its summary page.
Strategy summary pages have an overview, information about using the strategy in different learning environments, resources of interest, the factors this strategy supports, and related strategies you can explore. To view all the strategies in a content area, use the strategies tab at the top of the page. We'll look at all the Strategies for this learner model next.
The strategy page shows ALL of the strategies for that learner model. You can select factors of interest for you or your learners, and it will narrow the strategies to only those that match all of the factors selected. This makes it easy to find key strategies to better design for learner variability. Again, select the strategy name to visit its summary page.
Are you sure you want to delete this Workspace?
Enter the email address of the person you want to share with. This person will be granted access to this workspace and will be able to view and edit it.
Adjust the permissions of your Workspace.
This Workspace is .
This Workspace's Reflection Area is .
Learner variability is the recognition that each learner is a unique constellation of strengths and challenges that are interconnected across the whole child. Understanding these connections and how they vary according to context is essential for meeting the needs of each learner.
It disrupts the notion of a one-size-fits all education. Understanding learner variability helps educators embrace both students’ struggles and strengths as we connect practice to uplifting the whole learner.
Throughout the site, we talk about "factors" and "strategies." Factors are concepts research suggests have an impact on how people learn. Strategies are the approaches to teaching and learning that can be used to support people in how they learn best.
Use the Learner Centered Design Tool to build a workspace. Go to Learner Centered Design Tool.
Or, create a new blank workspace for your product or project.
Use one of the guided tools to build a workspace.
Or, create a new blank workspace for your product or project.
Make a copy of this workspace.
Redirecting soon...
Generating summary page
Loading...
On this page, using your heatmap, you will be asked to select factors to further explore, and then select new strategies you might incorporate into upcoming instruction. Once done, click “Show Summary" to view your Design Summary Report.
On this page, using your heatmap, you will be asked to select factors to further explore, and then select new strategies you might incorporate into upcoming instruction. Once done, click “Show Report” to view your Design Summary Report.
By selecting "Show Report" you will be taken to the Assessment Summary Page. Once created, you will not be able to edit your report. If you select cancel below, you can continue to edit your factor and strategy selections.
Announcement here
Item successfully added to workspace!
Issue adding item to workspace. Please refresh the page and try again.
Learner variability is the recognition that each learner is a unique constellation of strengths and challenges that are interconnected across the whole child. Understanding these connections and how they vary according to context is essential for meeting the needs of each learner. It embraces both students’ struggles and strengths. It considers the whole child.
Throughout the site, we talk about "factors" and "strategies." Factors are concepts research suggests have an impact on how people learn. Strategies are the approaches to teaching and learning that can be used to support people in how they learn best.
The Learner Variability Navigator is a free, online tool that translates the science of learner variability into factor maps and strategies that highlight connections across the whole learner. This puts the science of learning at teachers' fingertips, empowering them to understand their own practice and support each learner.